| 1.
There are many techniques for choosing the location of a small wind turbine.
Your main aim should be to have the wind turbine installed in place where
the winds are as strong and frequent as possible.
Do not try to locate the most suitable installation point using portable
anemometers. It is futile. Farmers, fishermen and permanent residents
of the area know best where the winds are strongest and most frequent.
Consult them...
In general, the following simple principles apply:
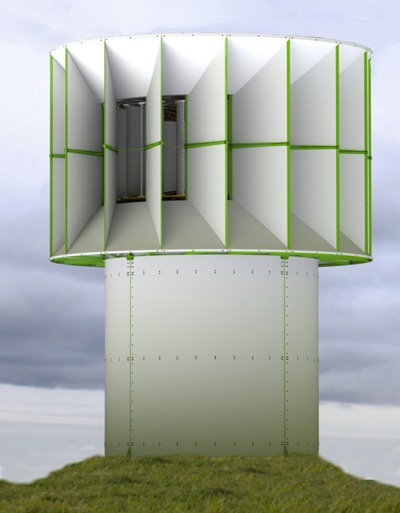
- At the installation point, around and near the wind turbine, there should
be no obstacles to the wind flow. The "Iasos" wind turbine can
work equally efficiently in any wind direction. Therefore it is not enough
to have no obstacles only in the direction from which you think the wind
usually blows. If you follow such a logic, the efficiency of the wind
turbine will be greatly reduced.
- The higher the wind turbine is from the ground, the greater its efficiency
will be, because as the height increases, the speed of the wind also increases.
But you don't need to resort to exaggerations, making special pedestals
and pillars. The turbine of the wind turbine is anyway than 2.5 m far
away from the ground. If you decide to build a raised pedestal, consult
a specialist engineer.
- From the following three methods of selecting a wind turbine installation
point, we recommend the second or third method:
a.
The first method, the scientific method, is based on detailed measurements
of the wind potential of the area where the wind turbine is to be installed.
It requires many months of scientific research and is expensive. This
method is followed by large companies that intend to invest a lot of money
installing horizontal axis wind turbines on mountain tops. One of the
advantages of this method is that the wind data concerns the installation
point of the wind turbine and not some other point or a wider area.
b.
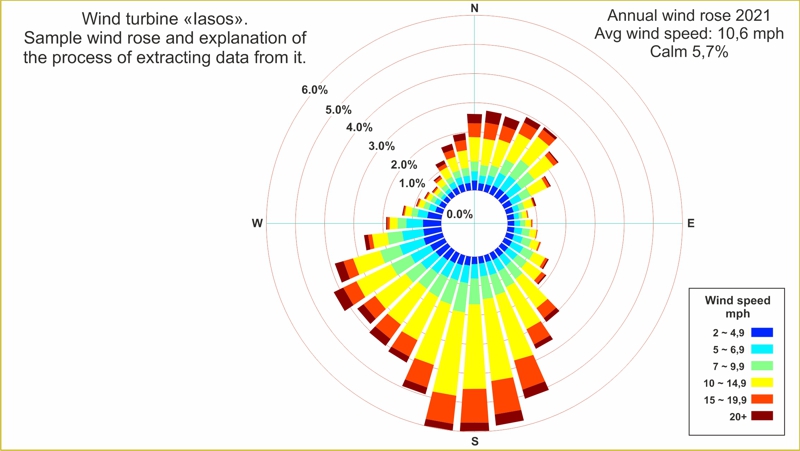
The second method is also scientific, but it costs almost zero. In this
method we use the wind data, as shown in the "wind rose" of
the area closest to the point where the wind turbine will be installed.
The results obtained using this method of estimating the wind potential
have only a small deviation from reality and are subject to almost the
same probability of verification as the data of the previous method. The
disadvantage of this method is that the "wind rose" probably
concerns an area that is quite far from the installation point of the
wind turbine. For example, it is easy to get the "wind rose"
of the nearest airport (which is usually located in a plain), but the
installation site of the wind turbine is not only far from the airport,
but on the other side of a hill...
In order to extract the wind data from "wind rose" and use it
to make estimates about the amounts of electricity that can be produced
by the "Iasos" wind turbine, you should download from our company's
website the special free software and the corresponding instructions for
use. You can also find a related video on our website.
The "wind rose" is a circle chart and looks like the one in
the next image.
c.
The third method is based on the use of a single parameter, that of the
"average annual wind speed".
From your country's weather service, try to get a wind potential map of
your area (one year long). Try to have the map refer to as recent a year
as possible. The wind potential map looks like the map in the next image.
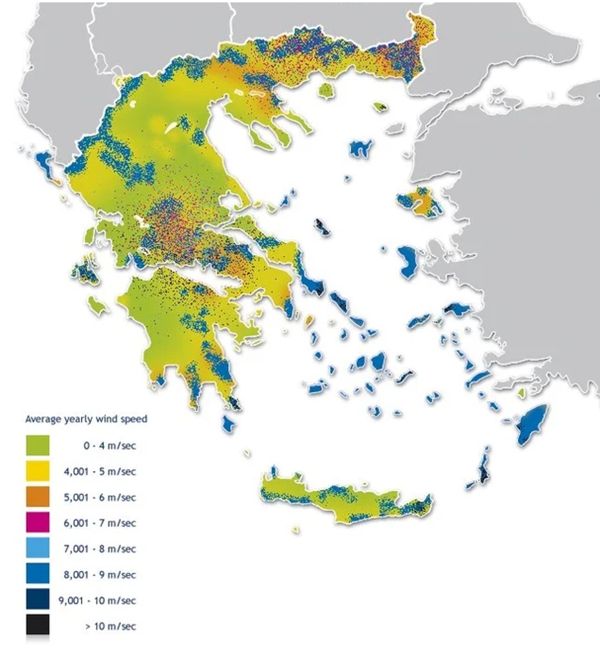
It is very easy and free of cost for everyone to locate the average annual
wind speed of their area on meteorological maps. The disadvantage of this
method is that the average annual wind speed of each region does not apply
uniformly to each geographical point of the specific region. There are
significant differences from one geographical point to another, in the
duration and intensity of the winds, depending on the morphology of the
ground. By moving the installation point of the wind turbine, even a few
meters, you may achieve a significant difference in the wind potential.
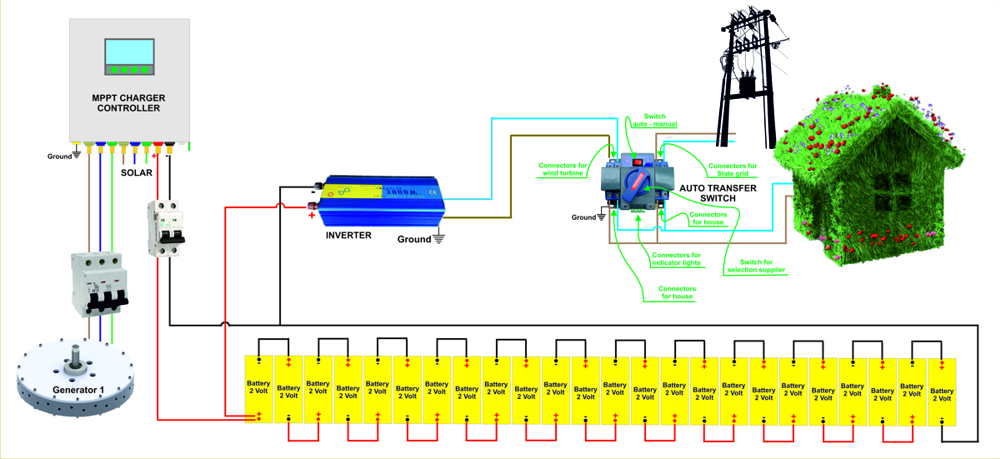
2.
You can install the wind turbine away from the point of consumption.
In this case, it is better to install the "charger controller",
batteries and "inverter" in the small room located at the base
of the wind turbine. This means that from the wind turbine you will get
220 Acv or 110 Acv, i.e., the "final electric current" for consumption.
Keep in mind that, on the one hand, the room at the base of the wind turbine
is not watertight, and on the other hand, it is very easy to be broken
into by someone.
Connect the wind turbine to the consumption (for example your residence)
using a simple three-conductor cable (for the scenario you get from the
220 ACV wind turbine). The cross-section of the ducts depends on the distance
between the wind turbine and the point of consumption (for example your
house).
The following table will help you choose the correct cable cross-section.
|